Workflows for data integrating into the infrastructure
To achieve the goal of a central infrastructure for data, NanoCommons created a concept and corresponding tools and workflows to collects, integrates and enhances data from a variety of providers and disseminates it to a variety of interested stakeholders in a manner that is FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable). The main idea is that data is only stored once in a public database / data warehouse optimised for this kind of data and it is then accessible via a common interface.
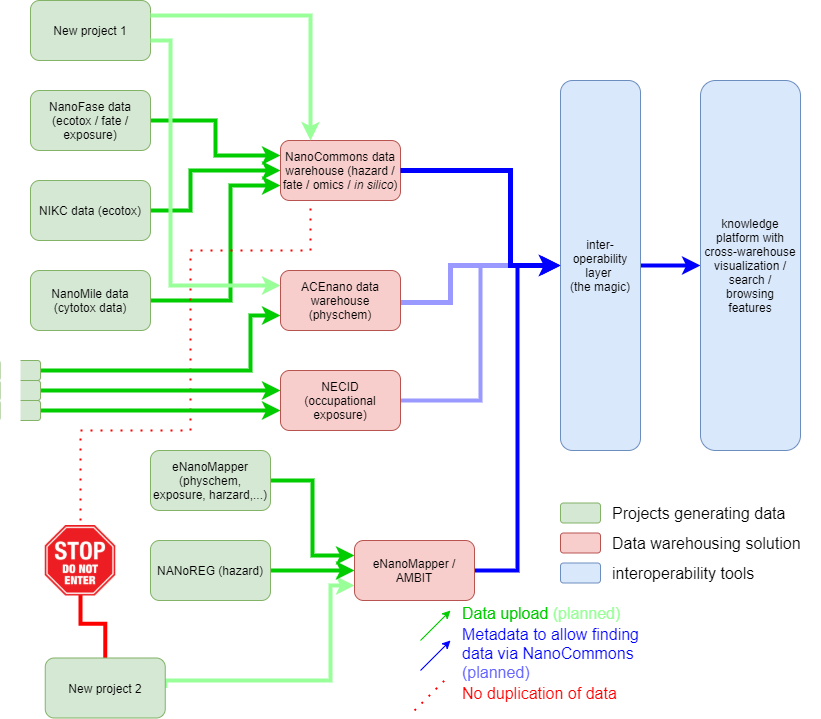 NanoCommons concept for a central data infrastruture: The data coming from different projects or individuals (green) are stored in one of the existing public and FAIR data warehouses including the Nanocommons Data Warehouse (red). The metadata describing the datasets are then harmonised int the interoperability layer and can be accessed under the common interface, the NanoCommons Knowledge Base (blue).
NanoCommons concept for a central data infrastruture: The data coming from different projects or individuals (green) are stored in one of the existing public and FAIR data warehouses including the Nanocommons Data Warehouse (red). The metadata describing the datasets are then harmonised int the interoperability layer and can be accessed under the common interface, the NanoCommons Knowledge Base (blue).
This is achieved by two possible routes depending on whether or not the data is already in a public database:
- NanoCommons partners work with managers of existing data warehouses, like eNanoMapper, NIKC and ACEnano, to generate semantic annotations of their data models, which can be used by the NanoCommons KB harmonisation layer for mapping and harmonisation between different databases. In this way, the NanoCommons KB will provide common search, browsing, and data enrichment functionalities across these databases allowing users of the NanoCommons KB to seamlessly access all available data across all linked databases via a single query or request. This will guarantee that the data is accessible in the NanoCommons KB as prepared in its original primary source (no losing of information or version mismatch), but is additionally annotated by detailed descriptors of the data format (data schemas) in a human- and machine-readable form allowing for automatic on-the-fly integration and combination of the resources in analysis and modelling workflows.
- A public data repository, called the NanoCommons Data Warehouse (DW), is being developed to host the datasets curated and/or analysed within the NanoCommons KB that are not currently publicly hosted elsewhere (i.e. are only on an individual researcher’s computer for example). This DW is fully integrated into the KB in the same way as the other databases for complete interoperability. This way, additional data can made effectively open and reusable on demand, based on agreement reached between the NanoCommons project and the users as stated in the conditions of use of the NanoCommons DW.
Combined, these two approaches are designed to reach a core goal of NanoCommons to support the European nanosafety community and NanoSafety Cluster (NSC) with making the large volumes of data generated over the last 10 years, as well as the datasets currently being generated in ongoing projects, accessible to the public. Due to variety of data types and the existing fragmentation of nanosafety data and spread over a variety of databases using different database concepts and models, clearly defined and easy to implement, but still flexible, workflows are needed to facilitate the integration of these existing databases and/or datasets into the KB. At the same time, ensuring the quality of the datasets, their completeness, and their harmonised utilisation of ontologies, such that similar nanomaterials (NMs) and measurement end-points can be queried successfully is also essential. Details on these workflows are available separately for the data warehouse integration in the NanoCommons KB and for individual dataset upload to the NanoCommons DW.