MODA for Calculations of Binding Free Energies and Potentials of Mean Force
Simulated in project SMARTNANOTOX
Overview of the simulation
1 User case
The purpose of these simulations is to determine binding free energy of a small molecule to a material surface in aqueous medium, as well as associated potential of mean force. The binding free energies are used further as descriptors of the material surface for interactions with biological matter.
2 Chain of models
- Model 1: Material surface (atomistic)
- Model 2: Sorbent molecule (atomistic)
- Model 3: Solvent molecule (atomistic)
3 Publication on the simulation
David Power et al 2019 Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 27 084003 doi:10.1088/1361-651X/ab3b6e
4 Access conditions
Open source CC-BY-3.0, https://bitbucket.org/softmattergroup/unitedatom/
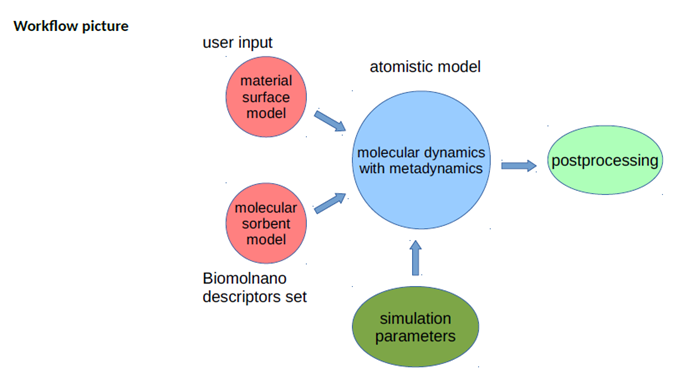
Workflow and its rational
The simulation takes two types of input: a model of material surface, which can be different and prepared by the user accounting for the structure, morphology, surface modifications/functionalization, etc, and a small molecule (from a predetermined set within the SmartNanoTox project) for which binding free energies are computed. Both models are described by molecular topology files (.itp files for Gromacs) and force field parameters. The potential of mean force is computed by Metadynamics version of atomistic molecular dynamics. The row output of the simulation program postprocessed after the simulation to get final potential of mean force and binding free energy